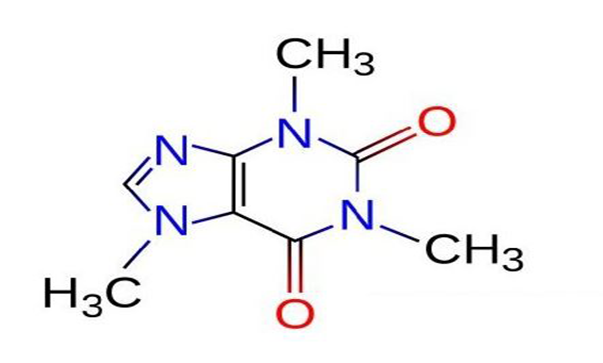
 Caffeine belongs to the class of methylxanthines.
Caffeine belongs to the class of methylxanthines.
It increases the aerobic capacity in a manner similar to the one of clenbuterol hydrochloride (bronchodilator- leading to the increase of VO2max).
It does not belong to the same class of substances (b-2 stimulants), but has the ability to cause bronchodilation, so in doses >3mg/kg acts an alternative solution for the treatment of paroxysmal asthmatic crisis.
Caffeine also stimulates smooth muscle layer of small intestine, which is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, so soon after we drink coffee with breakfast, an urge for defecation starts.
A fatal overdose of caffeine for a bodybuilder with a body weight of 100kg, is approximately around 10gr in a single dose (100mg/kg); while lethal levels in blood are found at around 80mg.
Death occurs from cardiac arrest due to ventricular tachycardia – fibrillation.
The intoxication of caffeine causes irritability-restlessness, tremor-trembling, rapid breathing-respiration, sweating, headaches, diarrhea syndromes, precordial chest pain and delirium.
The abuse and addiction to caffeine isthe most widespread and legal way of chemical enhancement, worldwide, on a daily basis.
Caffeine is able to pass through blood brain barrier and placenta.
Caffeine acts synergistically as a catalyst to ephedrine hydrochloride and enhances beta oxidation of fatty acids, consequently lipolysis of the subcutaneous tissue.
The peak of its concentration occurs within an hour, while its half-life is estimated around four hours.
Proper dosage is estimated at 3mg/kg of body weight (300mg for a 100kg athlete).
Even larger dosages (5mg/kg), increase the maximum strength and training intensity.
At normal doses, caffeine has effects on learning and memory, improving reaction time, alertness, attention and concentration.
Caffeine is quite often combined with pain killers, such as paracetamol and multiplies the masking pain effect.
It is also an antidote for a hangover crisis and migraine episode.
CAFFEINE